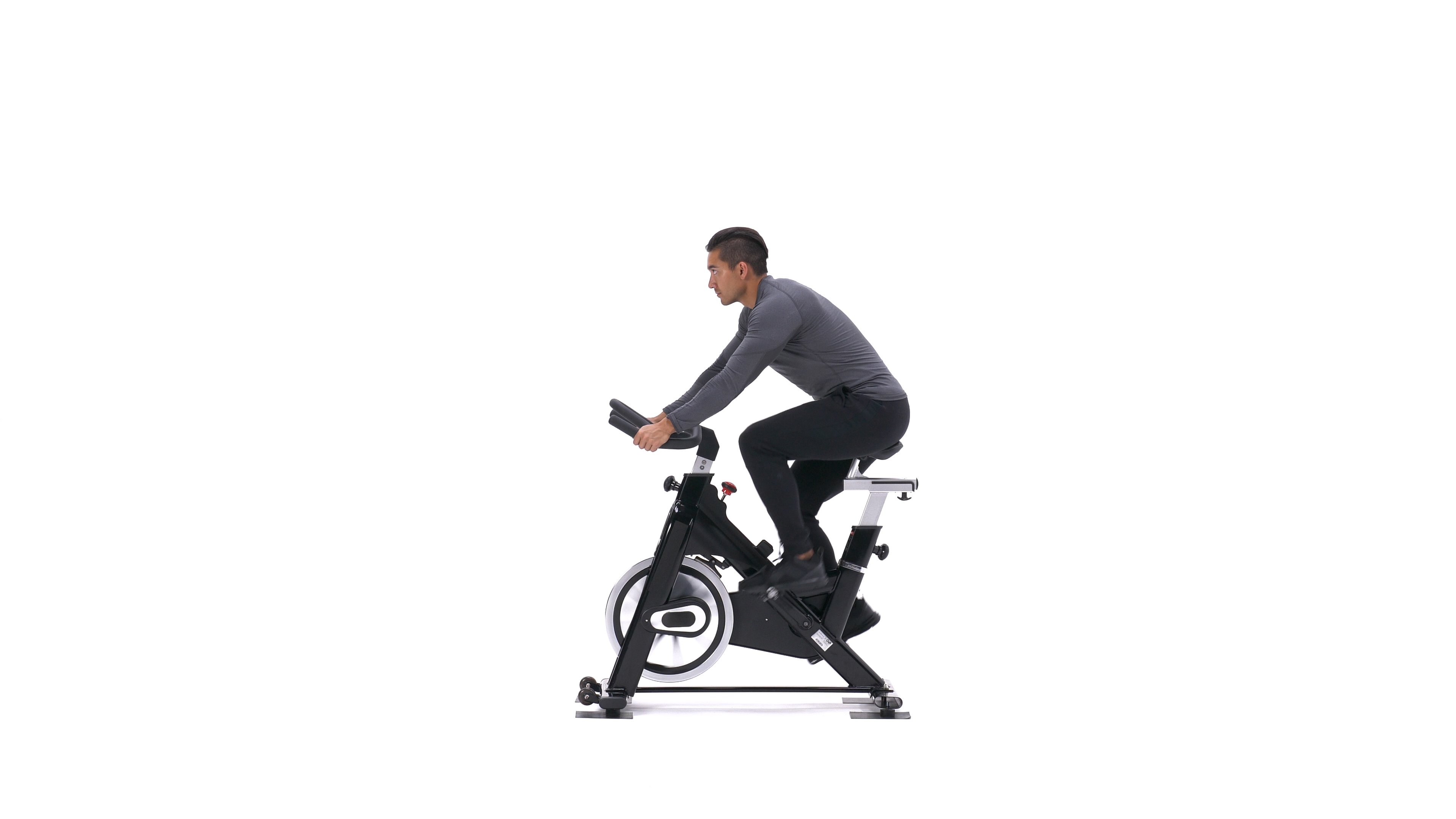
Stationary bike Images


Stationary bike Instructions
- To begin, seat yourself on the bike and adjust the seat to your height.
- Select the desired option from the menu. You may have to start pedaling to turn it on. You can use the manual setting, or you can select a program to use. Typically, you can enter your age and weight to estimate the amount of calories burned during exercise. The level of resistance can be changed throughout the workout. The handles can be used to monitor your heart rate to help you stay at an appropriate intensity.
Stationary bikes offer convenience, cardiovascular benefits, and have less impact than other activities. A 150 lb person will burn about 230 calories cycling at a moderate rate for 30 minutes, compared to 450 calories or more running.